Library
We are pleased to announce our new eBook/Audiobook service: Hoopla! Register now for access to eBooks, Audiobooks, Comics, Movies, TV Shows, and more.
The Learning Commons Library at Sauk Valley Community College offers resources and services to students and employees of the College, as well as residents of the SVCC College District, for education, information, and enjoyment.
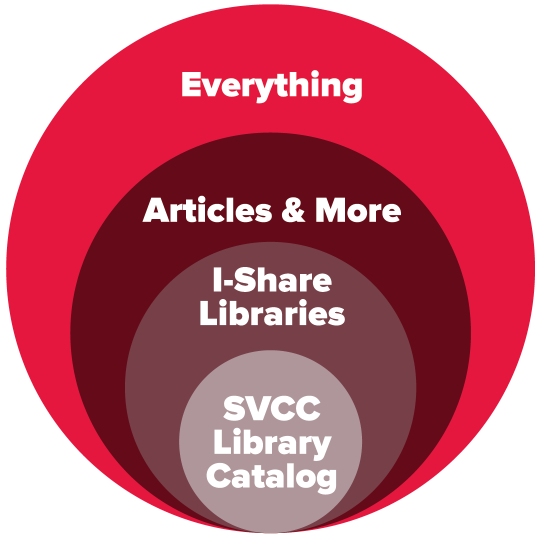
Search the Library Catalog
Tools for Success
Hours of Availability |
|
Fall/SpringMonday - Thursday Friday* |
SummerMonday - Thursday Friday |
|
*Virtual Hours Only |
|
Contact Information |
||
|
Room Number: |
Phone: |
Email: |